(Adding categories) |
|||
| Line 17: | Line 17: | ||
A patient with a sinus tract formation must be suspected for actinomycosis. |
A patient with a sinus tract formation must be suspected for actinomycosis. |
||
| + | |||
| + | [http://www.bestsinusinfectionremedies.net/sinus-infection-remedies-apple-cider-vinegar Sinus infection remedies apple cider vinegar] |
||
| + | |||
==Differential Diagnosis== |
==Differential Diagnosis== |
||
*Nocardiosis: does not produce sulfur granules |
*Nocardiosis: does not produce sulfur granules |
||
Revision as of 07:22, 15 January 2012
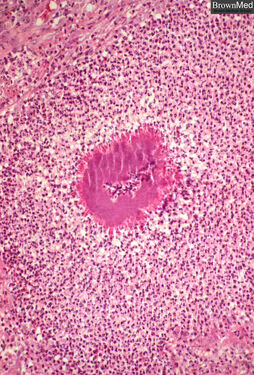
A sulfur granule is depicted in an abscess in a case of thoracic actinomycosis. The granules are composed of branched,gram-positive filaments of Actinomyces israelii. Though these organisms resemble fungi morphologically, they are bacteriaof the Order Actinomycetes; they are anaerobic. They lack mycolic acid in cell walls and thus are not acid-fast. From the slide collection of the late Dr. Charles Kuhn
"no disease is so often missed by experienced clinicians"
Actinomycosis is a slowly progressive, suppurative, fibrosing infection involving the jaw, thorax, or abdomen.the disease is due to Actinomyces. They are branching, filamentous, gram-positive rods that normally reside as saprophytes in the oropharynx, gastrointestinal tract, and vagina without producing disease. Actinomyces only causes disease is inoculated into anaerobic deep tissues which can occur after trauma produces tissue necrosis which leads to anaerobic medium for growth. There are four distinct sites where Actinomyces infection can occur:
- cervical facial actinomycosis: due to jaw injury, dental extraction or dental manipulation
- thoracic actinomycosis: due to aspiration of organisms contaminating dental debris
- abdominal actinomycosis: due to traumatic or surgical disruption of the bowel, especially the appendix
- pelvic actinomycosis: associated with prolonged use of intrauterine devices
The most common species is: Actinomyces israelii.
Epidemiology
Most commonly seen in males perhaps due to poor dental hygiene.
Clinical Manifestations
- Cervical facial abscesses: Most commonly follows dental extractions, manifesting as mandibular osteomyelitis or a soft tissue abscess. Pain is not a determining factor unless there is pus. Think about this etiology if a patient presents with a mass or relapsing infection in the head and neck.
- Thoracic actinomycosis: The lung may be involved after aspiration of infectious oral debris. Typical symptoms include fever, cough, sputum production, night sweats, weight loss, pleuritic pain, multiple sinuses that extend through the chest wall to the heart or abdomen.
- Abdominal Actinomycosis: Pain in the ileocecal region, spiking fever and chills, vomiting, weight loss, regular abdominal masses, pelvic inflammatory disease, sinuses draining to the exterior. Months will pass from the inciting infection to the clinical manifestations. Since the peritoneal flluid is infected, any intraperitoneal organ can be affected.
Suspect this etiology in patients with chronic pneumonia or indolent intra-abdominal or cervical facial abscesses.
A patient with a sinus tract formation must be suspected for actinomycosis.
Sinus infection remedies apple cider vinegar
Differential Diagnosis
- Nocardiosis: does not produce sulfur granules
- Lung cancer
- Tuberculous lymphadenitis
- Crohn's disease: draining sinus tracts may mimic inflammatory bowel disease
- Pelvic inflammatory disease from another cause
Diagnostic Workup
- Anaerobic culture: necessary to distinguish from Nocardia, usually takes 5 to 7 days the may take as long as 2 to 4 weeks
- Immunofluorescence
- Genotyping: 16S rRNA gene amplification and sequencing have been used to increase diagnostic sensitivity
Treatment
- Ampicillin
- Penicillin VK
- Therapy should be continued for weeks to months to ensure a cure
- Use CT and MRI to monitor treatment
Pathology
The critical point in infection is the disruption of a mucosal barrier. Actinomycosis starts as a nidus of proliferating polymicrobial organisms that attracts an acute inflammatory infiltrate. These small abscesses grow slowly and gradually become consolidated abscesses that are connected by sinus tracts that burrow across normal tissue boundaries and into adjacent organs. Eventually these draining sinus tracts can penetrate an external surface and lead to a draining sinus. Within the abscesses and sinuses are purulence and colonies of organisms that appear as sulfur granules because of their resemblance to elemental sulfur.
Histologically, the colonies appear as rounded, basophilic granules with scalloped eosinophilic borders

Actinomyces israelii. Gram stain from culture.Gut 2009;58:1062 doi:10.1136/gut.2008.164251a
Radiology
The radiographic pattern of actinomycosis is often indistinguishable from that of nocardiosis. This is an invasive disease that is capable of traversing tissue planes. Findings will be non-segmental airspace opacities in the periphery of the lower lobes, however in some cases the infection may manifest as a localized mass-like opacity that mimics bronchogenic carcinoma [1]. If there is extension into the pleural cavity it will lead to pleural effusion and then empyema while chest wall involvement may cause osteomyelitis (wavy periosteal lytic rib destruction). Rarely there may be a disseminated and miliary pattern. In abdominal disease there is heterogeneous enhancement of an abscess, mass, or mixed lesion with adjacent bowel wall thickening. Central nervous system disease is rare but will present with single or multiple brain abscesses that will appear as a ring enhancing lesion with a thick wall that may be irregular or nodular.
See also
http://www.brown.edu/Courses/Digital_Path/systemic_path/pulmonary/actino.html
- ↑ Kim SH, Kim SH, Yang DM, Kim KA (2004). "Unusual causes of tubo-ovarian abscess: CT and MR imaging findings". Radiographics 24 (6): 1575–89. doi:10.1148/rg.246045016. PMID 15537966.